Introduction
Plant phytoalexins are basically plant substances or chemicals produced by a plant after it is infected. These substances are produced as a result of plant defense mechanism which may be elicited by the invasion of a pathogen or in stressful conditions for example extreme temperatures etc. These plant phytoalexins can be terpenoids, glycosteroids or alkaloids depending on the type of pathogenic infection and the plant type. These substances act on the pathogen which is attacking the plant.
History
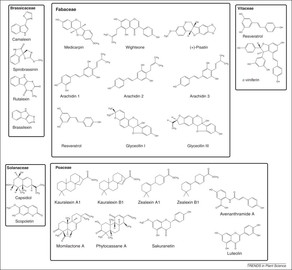
This class of plant antimicrobials was first discovered by K.O Muller and it was he who called these substances plant Phytoalexins. Muller was of the view that these chemical products were formed as a response to the elicitors, but could not be produced without the presence of infectious pathogen. He also was of the view that the production of these chemicals required the expenditure of plant energy mostly in the shape of genetic transcription or translation. Muller had to investigate the function of plant phytoalexins thoroughly so that they could fit the correct definition of an antimicrobial or antibiotic substance. A further requirement for a phytoalexin to be called an antimicrobial was to act as a basis of a disease resistance mechanism. After all this research the basic definition was coined which described a phytoalexin as a substance with a very low molecular weight and which was produced and accumulated by the plants in response to infections.
Features
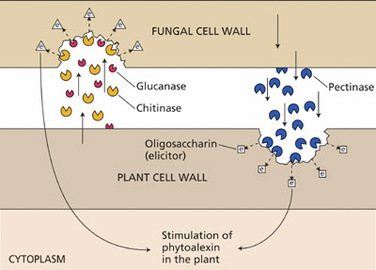
The basic mechanism of action of plant phytoalexins can be described as that of a substance which is highly toxic to the plant attacking organisms. This is justified by the following process by which these chemicals defend the plant against infections. The phytoalexin either punches small microscopic holes into the cell wall of the infectious organism or it either disrupts the maturation process of the pathogenic moiety. Phytoalexins can also hinder the reproduction system of the pathogenic substance as a result the plant becomes better resistant to all sorts of microbial infections. This is proven by the fact that the mutant plants which cannot produce phytoalexins are more prone to microbial infections and thus have extensive pathogenic colonization as compared to wild type of plants. A plant combats infections in two ways, long term and short term.
Tips and comments
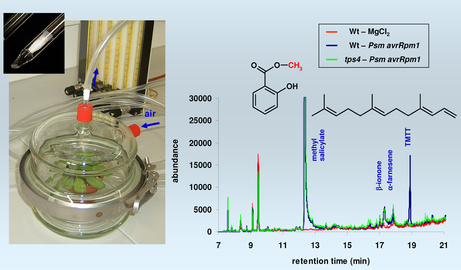
The long term defense mechanism involves the production of plant phytoalexins. This involves the coordination of the damaged plant tissue with the other parts of the plant. This is hormone mediated. Thus signals are transmitted to the genetic system of the plant and as a result the production of phytoalexins is triggered with the help of genetic transcription and translation. The accumulation of plant phytoalexins into the plant is only temporary as they are eventually degraded, hydrolyzed or polymerized with the help of an enzyme by the name of extracellular peroxides, which is also produced by the plant. Although the role of phytoalexins is still unclear but research has shown that the accumulation of phytoalexins at the site of infection, the increased activity of the enzyme responsible for its production and the fact that natural plants with phytoalexin producing properties grow better are some findings which definitely reinforce their importance for the plants.