Dutch Elm Disease
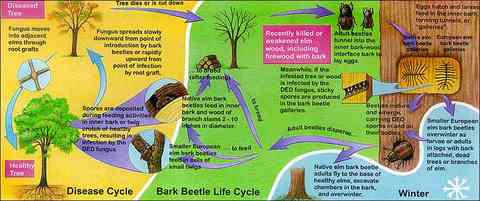
The U. S. Department of Agriculture claims the Dutch Elm Disease (DED) is one of the destructive diseases for shade trees. Once infected the trees do not survive for more than a few years. Elm trees are used in urban areas for the aesthetic value and shade. The damage from the disease is destroying the trees faster than they grow or can be replaced.
The elm trees manage to survive beyond the seed bearing years, but eventually succumb to the Dutch Elm Disease. DED is transmitted by elm bark beetles. Two types of beetles enjoy elm trees, the elm bark and the elm leaf. Only the elm bark beetles carry the fungus disease that destroys the tree. The elm bark beetle buries into the branch of the elm tree infecting the vascular system with the fungus. This fungus is transmitted through the vascular system into the roots and soil. The elms surrounding the area will become infected with the fungus. The following steps will help you to identify Dutch Elm Disease and differentiate it from other problems an elm tree may acquire.
Step 1
Check the crown of the tree for elm bark beetles. Dutch Elm Disease is distinguished by the wilting and yellowing of the leaves. The fungus causes a block in the vascular system of the tree. Water and nutrients cannot be carried to the branches and leaves. The lack of water will cause the leaves to turn brown and fall. Eventually the branches will starve and dry out.
Step 2
Check the roots and base of the tree for signs of damage. If the elm has been infected from the root system, the lower part of the tree will show signs of drying. The fungus may pass further up the tree, check the lower branches for damage.
Step 3
Check the branches and stems for a dark discoloration by peeling the bark off the limb you suspect of infection. Dutch Elm Disease travels through the vascular system. The fungus will cause discoloration. Depending on the thickness of the branch you will need to cut deeply. The fungus infects the sapwood, as the tree grows new sapwood will cover over the damaged areas. Cut a cross section of the branch and examine the rings for discoloration.
Step 4
Check each of the branches around the crown. Spring time is the growth time for all creatures and plants. The beetles may attack different limbs throughout the season. Dutch Elm Disease will flourish near the end of the Spring season spreading quickly through the tree.
Step 5
Distinguish between Dutch Elm Disease and other elm diseases by noting the symptoms. Yellowing leaves do not mean your elm tree has DED. Elm leaf beetles will feed on leaves cause dark spots and killing the leaves. “Elm yellows” affects the entire crown with yellow leaves that fall early, the inner bark turns tan, no discoloration of the inner wood, occurs in July to September, and emits a wintergreen odor from the inner bark. “Bacterial leaf scorch” is characterized by browning leaves with yellowing at the halo, beginning with older leaves. The wood and bark show no discoloration or a wintergreen scent.
Tips

Removing a branch from the crown of the tree and slicing in half will quickly determine if your elm has succumbed to Dutch Elm Disease.
The American Elm (Ulmus americana L.) is the most susceptible to Dutch Elm Disease. Other elms are affected at different rates and can be resistant.
To treat the disease, begin by interrupting the life cycle of the beetle. Insecticides are effective, but use caution, you do not want to kill beneficial insects. Research products that are beneficial to the environment and beneficial insects that will eat the beetle larvae. There are two types of elm bark beetles, the Native and European. The European is larger than the Native and both beetles burrow into the wood of the elm, laying eggs. Beneficial nematodes can be injected into the infected wood where they will feed on the eggs and larvae destroying the beetle before it reaches maturity.
Sources and Citations
Photo credits:
The Life Cycle of the Dutch Elm Disease: Artwork by Julie Martinez, Scientific Illustrator, St. Paul, MN
Branch flagging symptoms from a single point of Dutch elm disease infection in crown of elm. Photo courtesy of Dr. R. Jay Stipes
Haugen, L. How to Identify Dutch Elm Disease U.S. Department of Agriculture
Comments
Most Recent Articles
-
How To Manage Tall Fescue Toxicosis
Toxicosis is caused by a fungus that lives and grows between the cells of tall fescue plant. This fungus has no effect on the tall fescue plant. Toxicosis can also be caused by chemicals and...
-
Common Oak Tree Diseases
Like any other trees, oak trees are also susceptible to diseases. Oak tree diseases greatly affect the growth of the trees and may even cause the trees to eventually die. These oak tree dise...
-
How To Indentify the Symtoms Of Wetwood in Shade Trees
Wetwood or slime flux is a bacterial infection that affects shade and forest trees. Though it is not a very devastating type of disease, it can have adverse effects upon the tree's growth an...
-
Treatment Of Diseases Of Trees And Shrubs
There are a vast multitude of diseases that can effect trees and shrubs, which can either detract from their overall health or kill them. However there are methods in which you can undertake...