Introduction
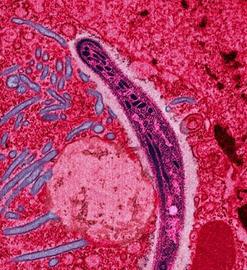
Communicable diseases, also known as infectious diseases, transmissible diseases and contagious diseases spread through transmission. This transmission can be through air, foods, random surfaces, animals and people. Communicable diseases rely on exchange of fluids, contaminated objects and close proximity to get transmitted from an infected person or object to a healthier individual. For example the disease transmission can be through sneezing, childbirth, blood transfusion or touching of a public object such as the railing at the subway. HIV, mumps, malaria, herpes, chicken pox, influenza are some well known diseases that come under this classification.
History
Scientifically speaking now, communicable diseases rely on pathogenic transfers. The mediums mentioned above are actually for transfer of these pathogens. Bacteria, viruses and parasites qualify as pathogens. To put it simply, pathogens are what we refer to as “germs”. It is these germs or pathogens that cause the disease. However, their mode of transfer, dormancy period, contagiousness and the danger they pose differs from disease to disease. Of course general immunity of the person being “attacked” can have a great influence as well. The basic aim of the pathogen is to enter the host that is the target body, survive under the presence of natural antibodies and multiply. It is this multiplication that causes them to take over the immune system and thus symptoms appear. After that the pathogens aim to transmit that disease to other healthier individuals through modes of transmission which explains why people insist on distance when they have a terrible cold.
Features

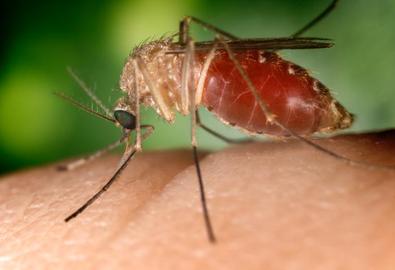
All in all communicable diseases are transmitted through a source. If the means of transmission is identified it can play an important role in identifying and thus preventing the disease before it takes over. Transmission of contagious diseases can include involvement of vectors. Vectors are of two types, mechanical and biological. This can be better explained through examples. A housefly is a mechanical vector which means it transfers the pathogen in a relatively passive manner, carrying it on the outside of its body via its appendages. This explains how food can get contaminated when flies sit on it for a while. On the contrary biological pathogens are carried within the bodies of vectors and are transferred through bites, as in the case of mosquitoes and malaria.
Tips and comments
The most basic way of preventing or slowing down the transmission of communicable diseases is to be able to recognize and identify characteristics and symptoms of various diseases. Human-to-human infectious diseases can be passed through mucus, blood, breast milk, saliva, uterine fluid, semen or breath. These can be prevented by frequent and thorough washing of hands, safer sex, better hygiene, avoiding bare touching of public surfaces, proper waste disposal, etc. Animal to human transmissions can cause malaria, rabies etc. It is advisable to stay clear of stray animals and insects and care should be taken when there are pets in the house. Getting vaccinated helps curb transmissions and strengthens the immune system. Methods and modes of transmission should be made well known to general public by health authorities.
Comments
Most Recent Articles
-
what is the most common communicable disease?
Communicable diseases are the infectious diseases, which are transmitted from one host to another. Such diseases are caused by some microscopic agents such as fungi, virus and bacteria. Thes...
-
List Of The Causes Of Communicable Diseases
Communicable diseases are diseases that are spread from one person to another, animal to person or vice versa and also animal to animal. Every person at one point in life is prone to these c...